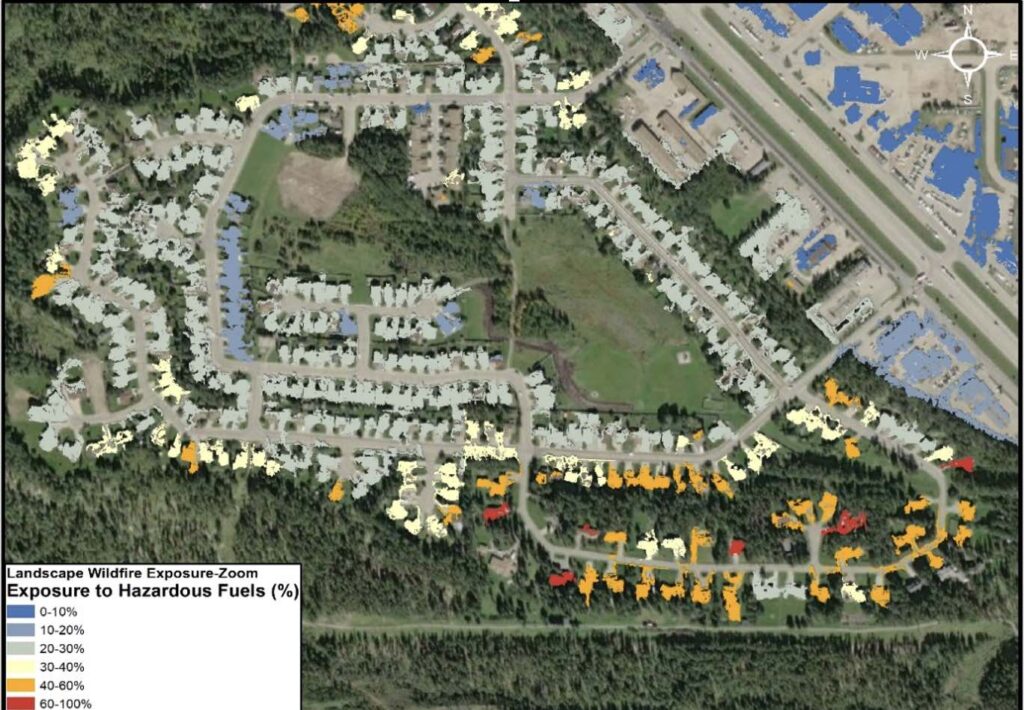
Traditionally, this is identified as the ‘Transition Zone’ between the wilderness and urban development. Essentially, where ‘environment meets human activity’. Watch the 3 Minute Satellite Moment below to hear this explanation.
Structures closest to the environmental border are at the greatest risk of catastrophic wildfire. This is often a result of three important considerations to monitor.
- Radiant Heat Zone– the area 0m – 30m (0 ft – 100ft) from environment to structures. This heat is intense and structural building materials often are not able to withstand this type of impingement.
- Short Range Embers – 30m – 100m (100ft – 300ft) Wind driven fires often carry these embers onto rooftops, towards back decks or dry yard areas where they can start new intense fires.
- Long Range Embers. 100m – 600m (300ft – 2000ft) Strong winds propel embers towards dry rooftops and backyards and tax municipal resources with spot fires.
At the Memphis Labs, we provide maps that with our computer modeling and identify where the greatest areas of risk are in the WUI.
With these priority zones identified, our solution based recommendations ensure clients use available mitigation funding effectively and efficiently.
We look forward to connecting with you to assist in developing your Wildfire Mitigation Plan.
Wildfire Monitoring doesn’t have to be expensive. As climate change causes greater swings in temperature, monitoring more regularly and effectively will provide the most accurate reports.
We use satellites to visualize earth at 0.5m (1.5ft) Our reports identify and classify the environment by fuel risk.
We look forward to working with your group!